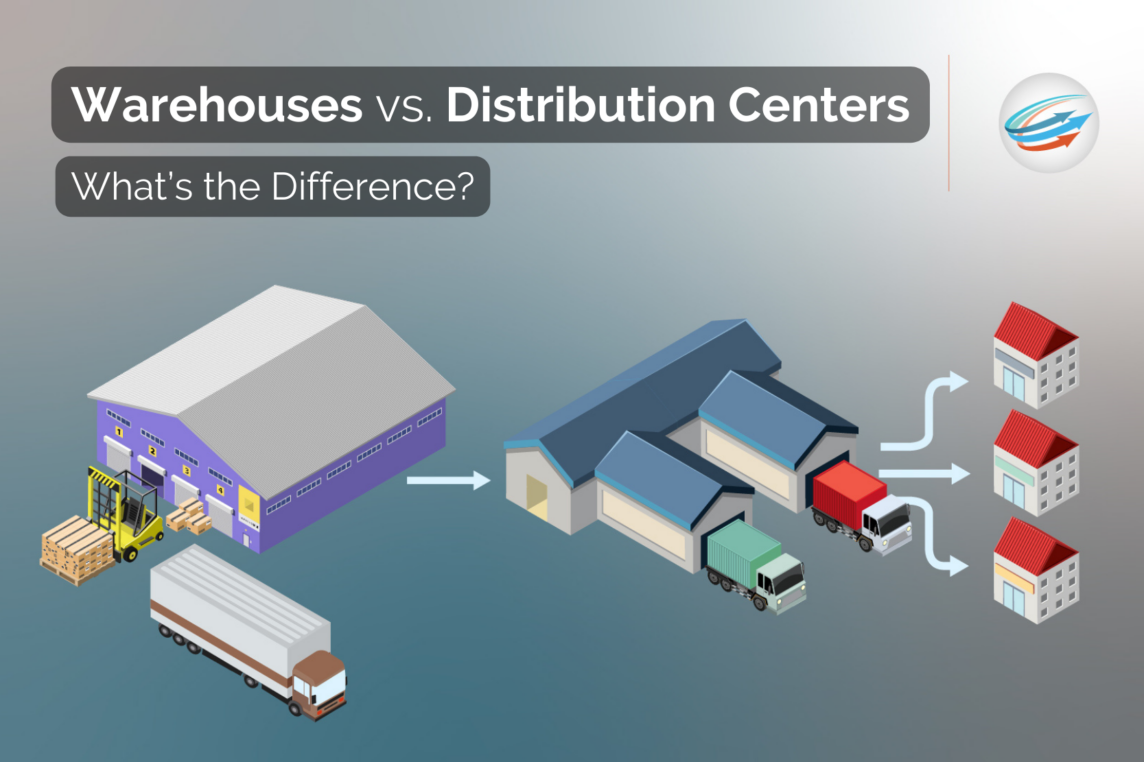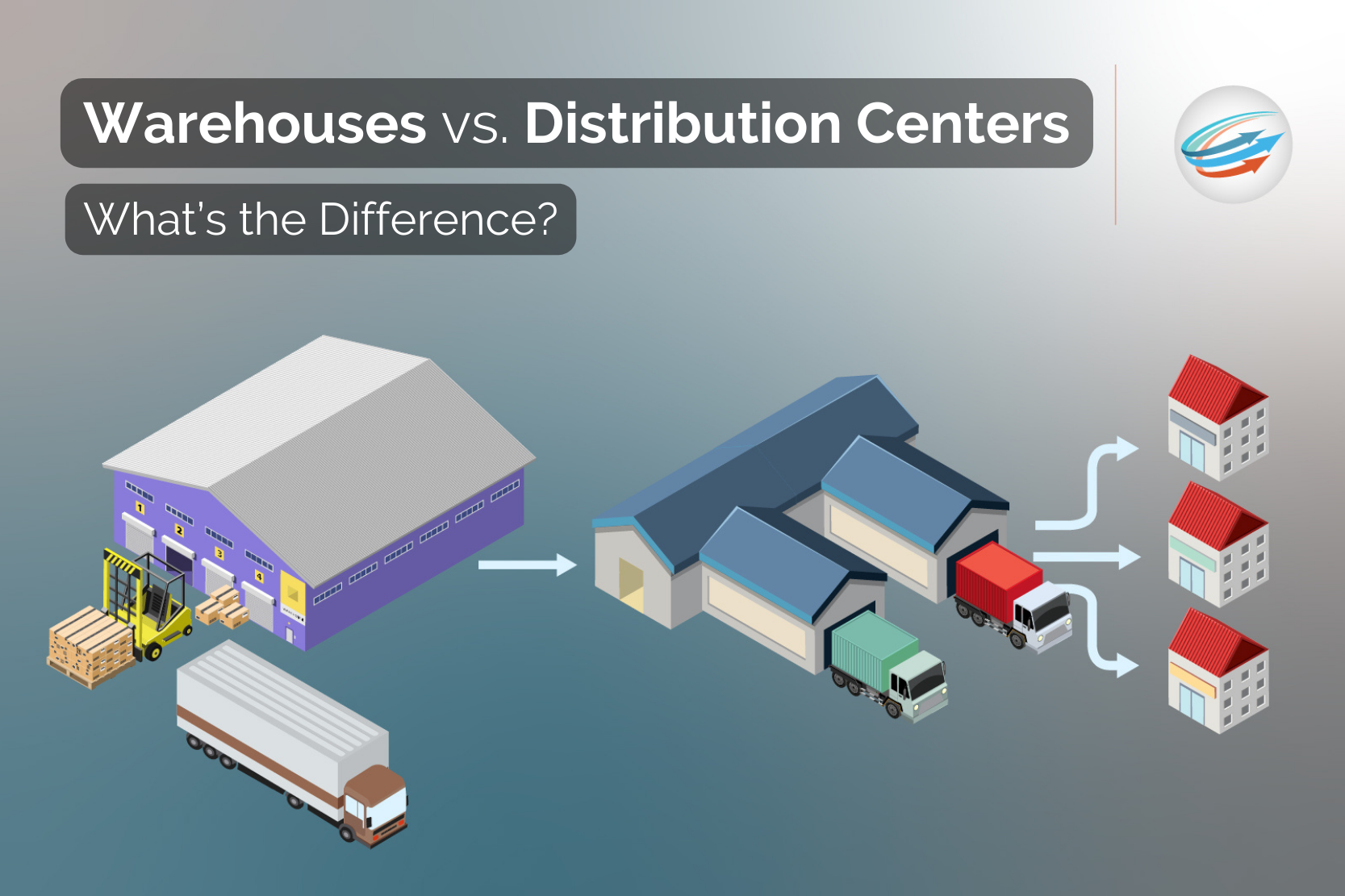
Have you ever wondered what the difference is between a warehouse and a distribution center? In today’s logistics space, warehouses and distribution centers are often used interchangeably—but they actually represent two very different functions. To help you understand the differences between these two facilities’ roles in the supply chain, we will go over their features, identify how each one serves a particular purpose within e-commerce operations, and outline their similarities as well as their individual strengths.
What Is a Warehouse?
A warehouse is a large structure used for the storage of goods and inventory. These facilities play a crucial role in the logistics industry as they provide a secure environment for products to be housed. Depending on the size of the warehouse, they may be used for short-term storage or long-term warehousing.
Many warehouses utilize various storage methods such as pallet racking, shelving, and mezzanine structures to maximize space efficiency. Stored goods range from raw materials to finished products and can be transported via trains, ships, or trucks.
Types of Warehouses
Warehouses can come in various forms, but the three main types of warehouses are private, public, and bonded warehouses.
- Private warehouses are often owned and operated by the company that uses them, providing complete control over their inventory.
- Public warehouses offer businesses a cost-effective option for their storage needs, with shared resources and affordable fees per square foot.
- Bonded warehouses allow international goods to be stored until they complete customs processes, with added security measures in place.
What Is a Distribution Center?
A distribution center is a crucial component of the supply chain that plays a pivotal role in getting products from the manufacturer to retailers or consumers. Generally, it acts as a storage facility for goods before they are shipped out to their intended destination.
In a distribution center, products are arranged into categories such as size, shape, or location and stored on pallets or shelves. The facility’s layout is designed to optimize the movement of products, so they are organized and easy to find when needed. Distribution centers employ sophisticated technology and software to manage inventory, reduce errors, and increase efficiency.
Types of Distribution Centers
There are various types of distribution centers, each tailored to meet specific logistics needs.
- Retail distribution centers primarily cater to delivering products directly to consumers. These centers are usually located closer to the end users to reduce delivery times and ensure that consumer demands are met promptly.
- Wholesale distribution centers are responsible for distributing goods in bulk to retail outlets and other wholesalers. These centers operate at a larger scale than retail distribution centers and handle a wide range of products.
- Cross-docking facilities specialize in unloading and quickly transferring products between trucks. Their primary goal is to eliminate the need for long-term storage and reduce the delivery time of goods.
Key Differences Between Warehouses and Distribution Centers
Understanding the differences between the two can help businesses make informed decisions about their supply chain strategy.
| Warehouses | Distribution Centers | |
| Role in the Supply Chain | A warehouse primarily stores goods until they are ready to be transported | A distribution center manages the movement of products within the supply chain |
| Activities performed | Receiving, storing, and shipping goods | Goes one step further by performing value-added services like packaging and assembly |
| Location and accessibility | Located in areas with lower land and labor costs | Strategically located near major transportation hubs |
| Types of products handled | Stores bulk items | Manage smaller items often packaged for individual consumption |
| Size and layout | Tend to be smaller and have a simpler layout | Tend to be bigger and utilize layouts designed for optimal efficiency and quick movement of products |
Similarities Between Warehouses and Distribution Centers
Warehouses and distribution centers are two essential components of the supply chain, and while they are distinct, they share many similarities.
The first and most obvious one is the fact that both are involved in the storage and movement of products. In other words, they are responsible for ensuring that the goods move seamlessly from the manufacturer to the end consumer.
Moreover, effective inventory management and tracking are essential to the success of both warehouses and distribution centers. In order to keep track of the movement of goods, companies rely on sophisticated systems that enable them to monitor and manage inventory in real-time.
Lastly, both are crucial to the overall success of the supply chain. Without these facilities, it would be impossible to move goods efficiently and economically from one point to another, ultimately affecting businesses and consumers alike.
Choose APS Fulfillment Inc. for Third-Party Logistics Services
APS Fulfillment, Inc. provides full-service third-party logistics services out of Miami. With years of experience in the logistics industry, we offer comprehensive services including inventory management, order fulfillment, and shipping. APS Fulfillment Inc. understands the importance of accurate and timely delivery, and we utilize state-of-the-art technology to ensure that tour clients’ needs are met.
Get in touch with us and one of our consultants will tailor a fulfillment plan designed to grow your business. Book a consultation by calling (954) 582-7450 or email [email protected].